Generative AI Foundations: Autoencoders, GANs, and Diffusion Models
Generative AI Foundations
Generative AI has revolutionized how we create content, from images and music to text and code. At the heart of this revolution are three fundamental architectures: Autoencoders, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), and Diffusion Models. Let's explore each of these powerful techniques.
1. Autoencoders (AEs)
Autoencoders are neural networks designed to learn efficient representations of data by compressing it into a lower-dimensional space (encoding) and then reconstructing it back (decoding).
Architecture
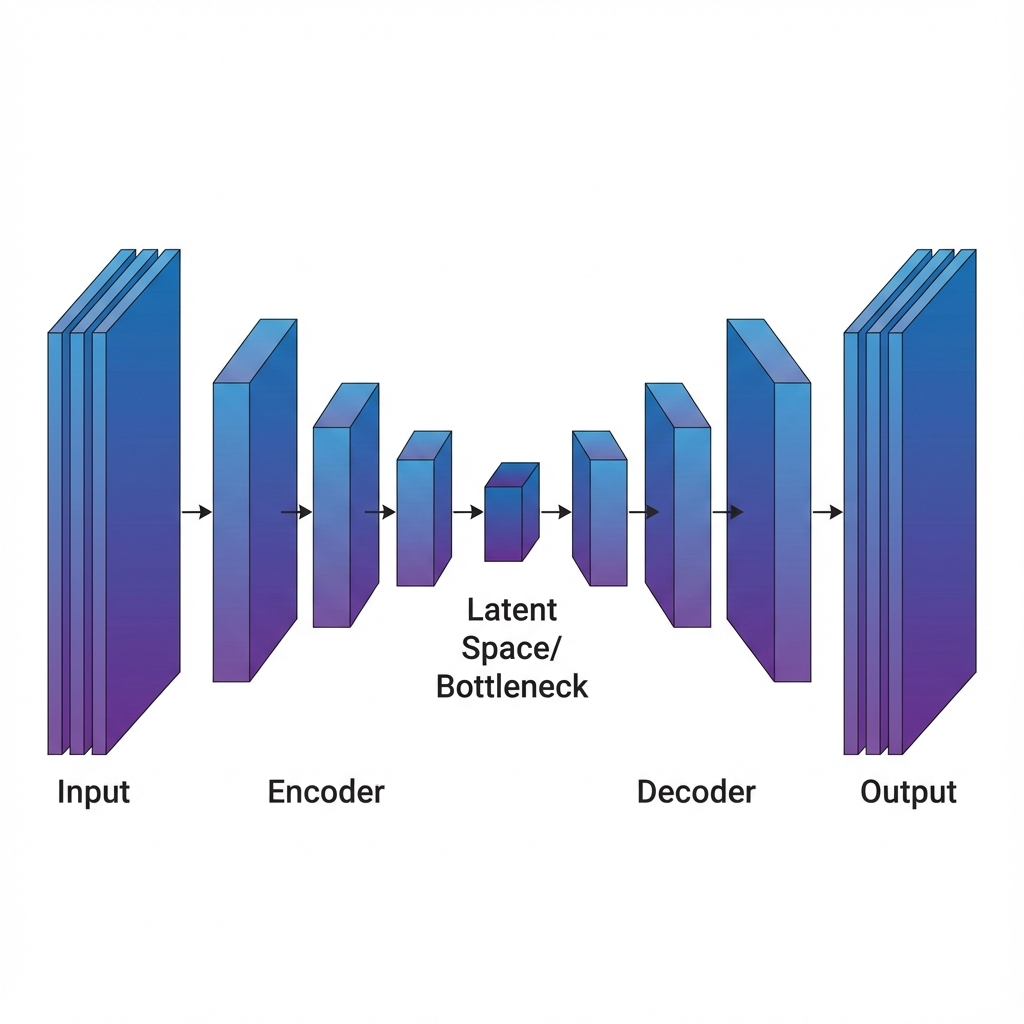
An autoencoder consists of two main components:
- Encoder: Compresses the input data into a latent representation (bottleneck)
- Decoder: Reconstructs the original data from the latent representation
Types of Autoencoders
Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs add a probabilistic twist to traditional autoencoders. Instead of encoding inputs as single points, VAEs encode them as probability distributions in the latent space.
Key Features:
- Learn a continuous latent space
- Enable generation of new samples by sampling from the latent distribution
- Use KL divergence to regularize the latent space
Denoising Autoencoders
These autoencoders are trained to reconstruct clean data from corrupted inputs, making them robust to noise.
Applications
- Image compression: Reducing file sizes while preserving quality
- Anomaly detection: Identifying outliers in data
- Feature extraction: Learning meaningful representations for downstream tasks
- Data denoising: Removing noise from signals or images
2. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
GANs introduced a game-theoretic approach to generative modeling, where two neural networks compete against each other.
Architecture
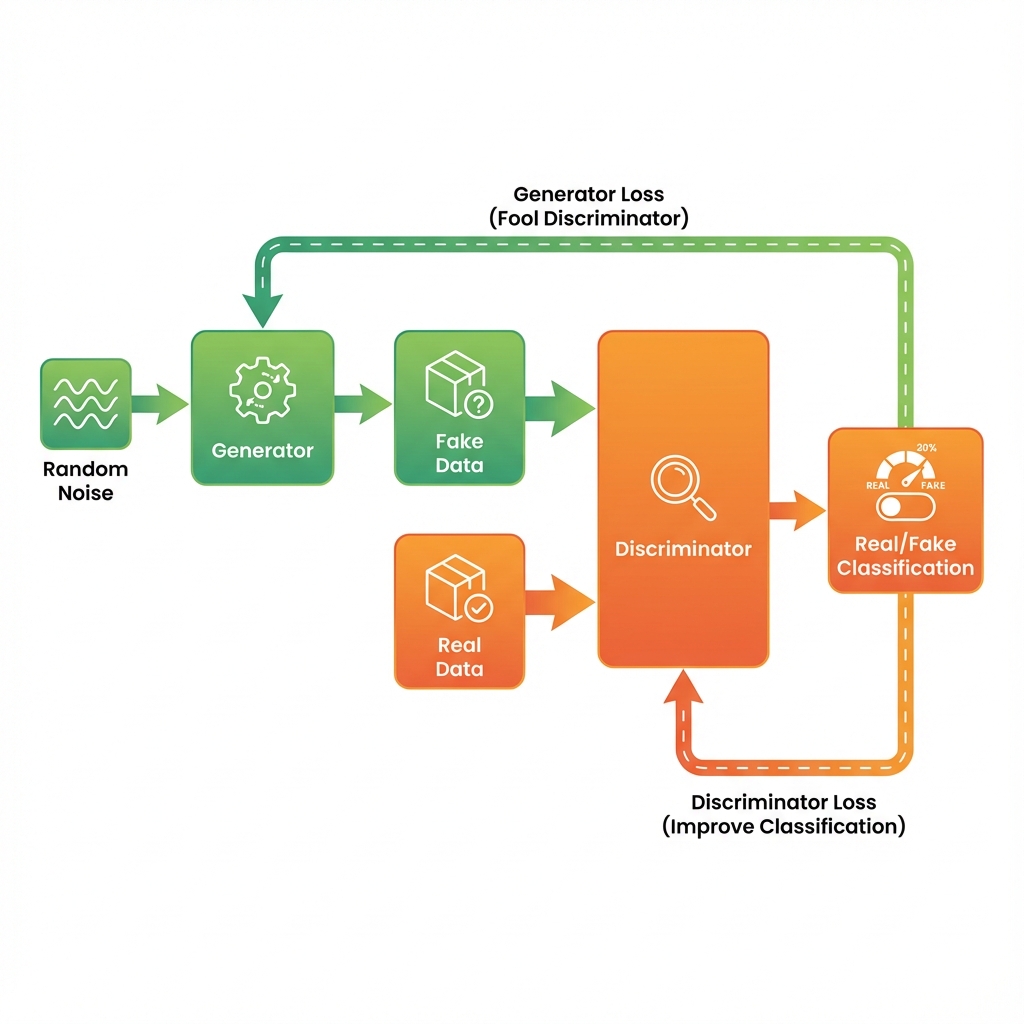
GANs consist of two networks:
- Generator (G): Creates fake data from random noise
- Discriminator (D): Distinguishes between real and fake data
Training Process
The training follows an adversarial process:
- Generator creates fake samples from random noise
- Discriminator evaluates both real and fake samples
- Generator improves based on discriminator feedback
- Discriminator gets better at detecting fakes
- Process repeats until equilibrium is reached
This can be expressed mathematically as a minimax game:
min_G max_D V(D,G) = E[log D(x)] + E[log(1 - D(G(z)))]
Popular GAN Variants
StyleGAN
- Generates high-quality, photorealistic images
- Allows fine-grained control over image features
- Used for face generation, art creation
CycleGAN
- Performs image-to-image translation without paired examples
- Applications: Style transfer, season conversion, photo enhancement
Pix2Pix
- Conditional GAN for paired image-to-image translation
- Applications: Sketch to photo, day to night conversion
Applications
- Image generation: Creating photorealistic faces, artwork
- Style transfer: Converting images between artistic styles
- Data augmentation: Generating synthetic training data
- Super-resolution: Enhancing image quality
- Video generation: Creating realistic video sequences
Challenges
- Mode collapse: Generator produces limited variety
- Training instability: Difficult to balance G and D
- Evaluation metrics: Hard to quantify generation quality
3. Diffusion Models
Diffusion models have emerged as the state-of-the-art approach for high-quality image generation, powering tools like DALL-E 2, Stable Diffusion, and Midjourney.
How They Work
Diffusion models work through two processes:
Forward Process (Diffusion)
Gradually adds Gaussian noise to data over T timesteps until it becomes pure noise:
q(x_t | x_{t-1}) = N(x_t; √(1-β_t) x_{t-1}, β_t I)
Reverse Process (Denoising)
Learns to remove noise step by step, generating data from pure noise:
p_θ(x_{t-1} | x_t) = N(x_{t-1}; μ_θ(x_t, t), Σ_θ(x_t, t))
Key Variants
DDPM (Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models)
- Original formulation with fixed noise schedule
- High-quality generation but slow sampling
DDIM (Denoising Diffusion Implicit Models)
- Deterministic sampling process
- Faster generation with fewer steps
Latent Diffusion Models (Stable Diffusion)
- Performs diffusion in compressed latent space
- More efficient than pixel-space diffusion
- Enables text-to-image generation with CLIP guidance
Applications
- Text-to-image generation: Creating images from text descriptions
- Image editing: Inpainting, outpainting, style editing
- Super-resolution: Upscaling images with fine details
- 3D generation: Creating 3D models from text or images
- Video generation: Generating coherent video sequences
Advantages
- High-quality outputs: Superior image quality compared to GANs
- Training stability: More stable than GAN training
- Flexible conditioning: Easy to incorporate text, class labels, or other conditions
- Diversity: Generates diverse outputs without mode collapse
Comparison
| Aspect | Autoencoders | GANs | Diffusion Models | |--------|-------------|------|------------------| | Training | Straightforward | Unstable | Stable | | Quality | Moderate | High | Very High | | Speed | Fast | Fast | Slow | | Diversity | Limited | Can suffer mode collapse | High | | Control | Limited | Moderate | Excellent | | Use Case | Compression, features | Realistic generation | High-quality generation |
Conclusion
Each generative model architecture has its strengths:
- Autoencoders excel at learning compressed representations and are great for dimensionality reduction and anomaly detection
- GANs produce high-quality, realistic outputs quickly but can be challenging to train
- Diffusion Models currently lead in generation quality and stability, though they're computationally intensive
The choice between these models depends on your specific requirements: speed, quality, training stability, and the nature of your data. As the field evolves, we're seeing hybrid approaches that combine the best of these techniques, pushing the boundaries of what's possible in generative AI.
Further Reading
- Attention Is All You Need - Transformer architecture
- Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Models - DDPM paper
- High-Resolution Image Synthesis with Latent Diffusion Models - Stable Diffusion
- Generative Adversarial Networks - Original GAN paper
Happy generating! 🎨✨